While on an official assignment i was
asked to deploy open source Network Management System on the windows
platform. While working on the task i got some problems and issues for
which i was not able to find solution on internet and i got solution
using hit and trial method. And then I thought to write on these
problems and their solutions. But at the first step I will write step by
step guide to install the of OpenNMS on Windows Platform (i.e. Windows
XP or Win Server 2003)
Installation of OpenNMS will consist of 4 steps,
1. Installation of Java Development Kit
2. Installation of PostgreSQL
3. Initialize the Database
4. Adding JRRD library
5. installation of OpenNMS
1. Installation of Java Development Kit
- Download the latest version of Java SE JDK from Java official website java.sun.com
- Remember JDK is not just JRE and you need to download Java SE (Standard Edition) and not Java EE or Java ME or Java FX.
- Run the JDK installer and it will ask for the License Agreement.
- Click Next and installation will begin.
- Press the Finish button to complete the installation of Java SE JDK.
- Download the one click installer of PostgreSQL for windows from http://www.postgresql.org/download/windows and run the setup.
- Click next to proceed the installation
- If it is required to change the destination path then select the installation directory, or simply press Next to proceed.
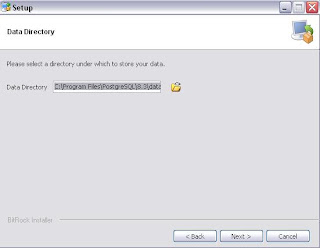
- If it is required to change the destination Data Directory path then select the directory, or simply press Next to proceed.
- Enter the password for the Superuser and Service account i.e. POSTGRES and press Next.
- Enter the Server Listening port (Recommended to use the default port), and press Next.
- Choose appropriate Locale or use Default locale and press Next.
- Setup is now ready to install. Press Next to start installation.
- Wait till the installer continues and finish screen appears.
- Press the finish button to complete the installation.
3. Initialize the Database
- If for any reason during the installation default database is not initialized then it can be done manually. Open the command prompt and go to the Bin directory of PostgreSQL. In my case it is "C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\8.3\bin"
- Initialize the database by using the following command "initdb -E UTF-8 -U postgres ..\data"

- If "../data exists but is not empty" message appears then it means the Database is already initialized.
- Run the Server by going to Start Menu --> Programs --> postgresql 8.X and click Start Server.
- Follow the same path and click pgAdmin III.
- Double click on postgresql 8.X (localhost:5432) to connect to the Database.
- It will prompt for the password. Enter password and press OK button.
- Select the postgres Database by following Databases --> Postgres.
- Go to the file menu and select Options.
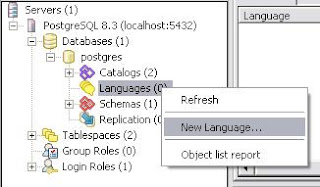
- Under the Display tab activate the Languages as shown above, and press OK button.
- Go back to the database postgres and expand it. Now Languages option will be available under tree. right click Languages and select New Language.
- From the Name drop down menu select plpgsql and press OK button to add the language.
- Exit pgAdmin.
4. Adding JRRD Library
- Now JRRD is no longer distributed as part of OpenNMS. If you want to be compatible with RRDTool instead of JRobin then download JRRD from here.
- Add library to the path variable.
- Download latest version of standalone-opennms-installer-X.X.X.jar from the OpenNMS download page.
- When download is finished then double click the Jar installer and it will start installation. If internet explorer saves the file as a ZIP file which contains different folders then it means that you have not installed java SDK.
- Click Next.
- Accept the license agreement and press Next button.
- Select JDK home directory and select Next.
- Select Installation directory and select Next.
- Enter postgres user password and press Next.
- Enter IP range to Discover nodes and press Next.
- Press Next.
- When installation completes press Next button.
- When configuration and database installation completes press Next.
- Click Done to finish the installation.
- Open the command prompt and goto the openNMS bin directory. by default it would be C:\program files\opennms\bin
- If you are installing the JRRD separately and your JRRD.jar file is placed at c:\opennms\lib then run following command
install.bat -disl "c:\opennms\lib"
- Execute the following command
opennms.bat start
- open your browser and open the link http://localhost:8980/opennms
- Use admin user name and admin password to login to the web console.
- and you are ready to Go with OpenNMS