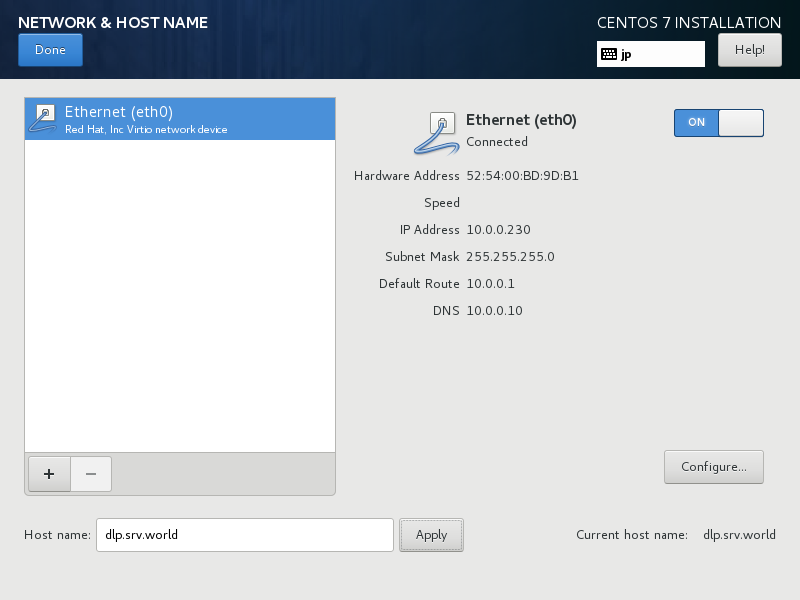
| [root@node01 ~]#
docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
web_server latest b7cf7440922c 4 minutes ago 306.4 MB
docker.io/centos latest 98d35105a391 3 weeks ago 192.5 MB
# create a service with 2 repricas
[root@node01 ~]#
docker service create --name swarm_cluster --replicas=2 -p 80:80 web_server:latest
7xg4yssy516xwgkjx2vxbw05d
# show service list
[root@node01 ~]#
docker service ls
ID NAME REPLICAS IMAGE COMMAND
7xg4yssy516x swarm_cluster 2/2 web_server:latest
# inspect the service
[root@node01 ~]#
docker service inspect swarm_cluster --pretty
ID: 7xg4yssy516xwgkjx2vxbw05d
Name: swarm_cluster
Mode: Replicated
Replicas: 2
Placement:
UpdateConfig:
Parallelism: 1
On failure: pause
ContainerSpec:
Image: web_server:latest
Resources:
Ports:
Protocol = tcp
TargetPort = 80
PublishedPort = 80
# show service status
[root@node01 ~]#
docker service ps swarm_cluster
ID NAME IMAGE NODE DESIRED STATE CURRENT STATE ERROR
78lh8sn1myw... swarm_cluster.1 web_server:latest node01.srv.world Running Running about a minute ago
4ag74wr59rb... swarm_cluster.2 web_server:latest node03.srv.world Running Running about a minute ago
# verify it works normally
[root@node01 ~]#
curl http://node01.srv.world/
Docker Node : node03.srv.world
[root@node01 ~]#
curl http://node01.srv.world/
Docker Node : node01.srv.world
[root@node01 ~]#
curl http://node01.srv.world/
Docker Node : node03.srv.world
[root@node01 ~]#
curl http://node01.srv.world/
Docker Node : node01.srv.world |